Higher average annual temperatures, coupled with increasingly affordable air conditioning units, are helping device-controlled room air conditioning to grow in popularity.
However, such appliances not only create a pleasant climate, but also bring with them special requirements in terms of maintenance.
In addition to the requirements for proper operation, there are a large number of legal regulations that must be observed. These can be found, for example, in the Employee Protection Act, the Construction Workers Coordination Act, the Workplace Ordinance or the Refrigeration Ordinance, to name just a few of the most important legal provisions. A detailed list with further legal bases can be found at the end of the blog entry.
Which regulations for air conditioning appliances does the legislator prescribe?
Refrigeration Plant Ordinance
Applies to businesses in which refrigeration, air conditioning and heat pump systems with a refrigerant charge weight of more than 1.5 kg are used.
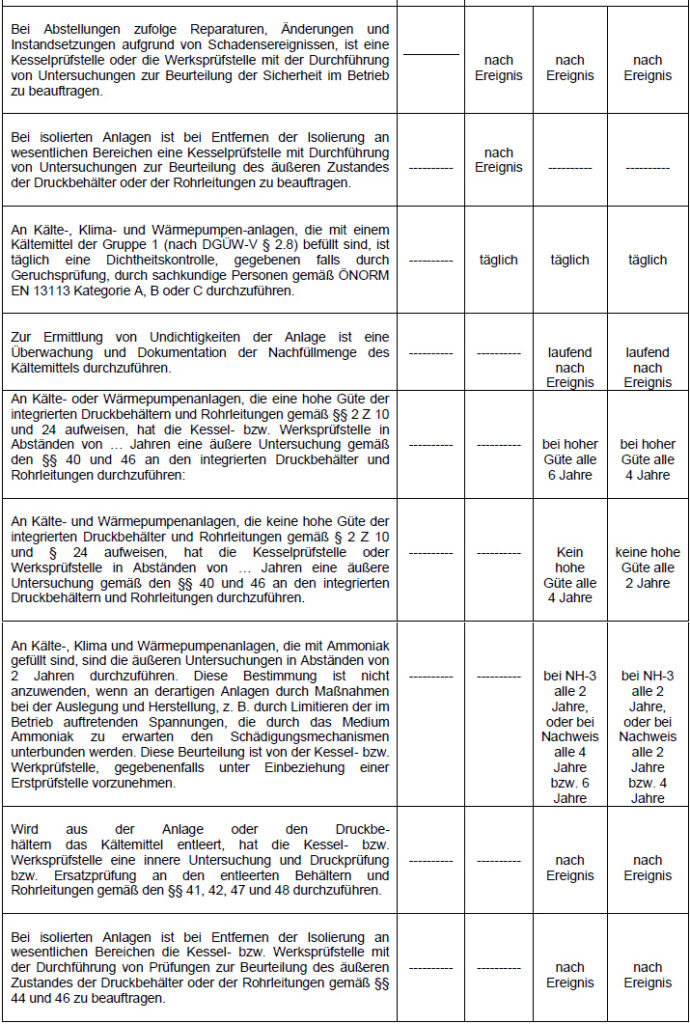
In accordance with § 22, these systems must be subjected to a safety inspection by competent personnel in accordance with Ö-NORM 13313 category B or C after major malfunctions, major repair work and all modifications, but in any case at intervals of no more than 1 year.
The maintenance and inspection work carried out is entered and confirmed in the inspection and system logbook.
This book must be kept in the workplace for the entire service life of the system and must be available to the competent personnel and the authorities at all times.
Workplace Ordinance
According to the above-mentioned regulations, an inspection must be carried out at least once a year or at least every 15 months to ensure that the equipment is in proper condition.
If there is an inspection and system logbook, the repair and inspection work carried out can be recorded there; if this is not available, records must be kept and stored in the workplace for at least 3 years.
Pressure Equipment Monitoring Ordinance
The Pressure Equipment Monitoring Ordinance (DGÜW-V) and the existing hazard potentials must be subjected to an initial operational test on commissioning and periodic inspections (“monitoring”) by boiler inspection bodies during operation in accordance with the provisions of §3 of the Pressure Equipment Monitoring Ordinance.
The operator of a pressure device with a high hazard potential must commission a boiler inspection body for the inspection and testing.
Depending on the type of refrigerant, these are divided into 2 groups:
Regulation EC-NR 2037/2000
Applies to all hydrofluorocarbons (HCFCs), e.g. R22.
All refrigeration and air conditioning systems with a filling weight of this refrigerant of more than 3.0 kg must be subjected to a leak test once a year by qualified personnel in accordance with Ö-NORM 13313 category A, B or C.
Regulation EC-NR 842/2006
Applies to all systems with fluorinated greenhouse gases.
The operator of these systems must have the tightness of the systems checked by qualified personnel in accordance with Ö-NORM EN 13313 and confirmed in the test and system logbook.
Different intervals apply depending on the size of the systems.
Systems with 3 kg of refrigerant should be checked for leaks at least every 12 months, systems with 30 kg of refrigerant every 6 months and systems with 300 kg of refrigerant every 3 months.
Building Directives 2010/31/EU
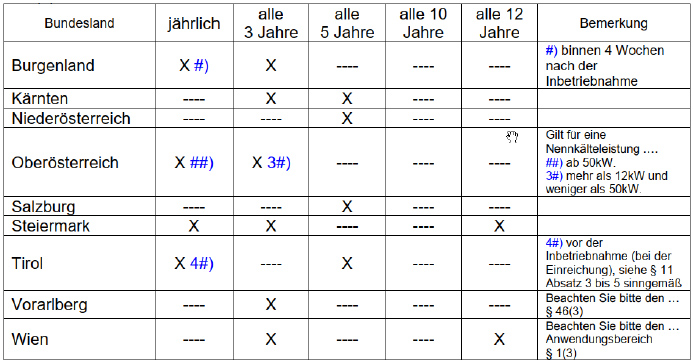
The building directive is regulated differently in the state laws of the respective federal states. In general, it can be stated that, depending on the size of the facilities, corresponding inspections must be carried out every three years, five years or 12 years on the basis of the Buildings Directive. The respective state laws also regulate which inspections must be carried out.
The above excerpts from the respective ordinances are only an abridged version and therefore do not represent the entire content of the corresponding ordinances and standards.
Why service air conditioning units?
In order to extend the service life of the system and keep energy costs as low as possible, regular maintenance should be carried out by trained personnel. Regular maintenance also benefits your health, as bacteria, viruses and fungi are regularly removed.
What needs to be considered for refrigeration systems?
According to the Refrigeration Ordinance, refrigeration systems must correspond to the current state of the art and must not impair the protection of the life and health of employees, the neighborhood or the environment.
The refrigeration systems must therefore be kept in an appropriate condition during operation and any defects must be rectified immediately.
Regular inspections must be demonstrably carried out by competent personnel.
For systems with a refrigerant charge of more than 0.5 kg, operating instructions in the local language must be available on site (brief operating instructions)
A test and system log must be kept for all refrigeration systems with a capacity of more than 1.5 kg. This must contain all initial tests, instructions, inspections, control and labeling obligations including results.
From a refrigeration charge of 1.5 kg, the operating instructions or the instruction of the owner of the operating system or the user must demonstrably include which periodic inspections in accordance with the above-mentioned regulations are applicable and must be carried out. of the above-mentioned regulations are applicable and must be carried out.
The maintenance intervals should be reduced in rooms with high hygiene requirements (doctors’ surgeries etc.) or with high levels of air pollution.
What maintenance work should be carried out on air conditioning systems?
- Pressure cleaning
- Checking and cleaning the condensate pump
- Checking the refrigeration circuit for leaks
- Testing the switching sequences
- Checking the safety circuit
- Removal of residues
- Cleaning the condensate, line and air filters
- Measurements of evaporation and condensation
- Measurement of the current consumption of the compressor
- Disinfection of the evaporator
- Condensate pump Clean test
- Measure evaporator temperature
- Final, visual and insulation inspection
- Check and clean fan, roller / ventilator
- Entry of maintenance in the refrigeration test logbook
(No claim to completeness, detailed questions must be agreed with the relevant specialist company).
Our tip for the professional operation of an air conditioning unit…
The operation of an air conditioning unit involves a large number of conditions and maintenance requirements that must be complied with. These may be imposed by the manufacturer or the legislator. In order to comply with this as a system operator or building owner, regular and proper maintenance is essential. Our MyBuilding24 app helps you to keep track and never miss a maintenance task again. Furthermore, all work can also be documented in order to meet the requirements of the system logbook.
Glossary
Legal basis
- ASCHG Employee Protection Act
- BauKG Construction Workers Coordination Act
- KGCHG Consumer Protection Act
- AStW Workplace Ordinance
- B-AStV Federal Workplace Ordinance
- KAV Refrigeration Plant Ordinance
- DDGV Dual Pressure Equipment Ordinance
- DGÜW-V Pressure Equipment Monitoring Ordinance
- AM-VO Work Equipment Ordinance
- MSV2010 Machinery Safety Ordinance
- Regulations (EU) 517/2014 on fluorinated greenhouse gases and repealing Regulation (EC) No 842/2006
- Regulation (EC) No. 1005/2009 on substances that deplete the ozone layer
- 9 different state ordinances
- FIEC 60335-2-40 Household and similar electrical appliances – Safety – Part 2-40
- Ö-NORM EN378 Refrigeration systems and heat pumps
- ÖNORM 7379 Gas storage
- VDMA 24246 Safety and environmental requirements for refrigeration systems and heat pumps
- Electrical Engineering Act and provisions of the associated electrical engineering ordinances
- Municipal energy efficiency program: Air conditioning systems with a total cooling capacity of more than 12 kW must undergo regular inspections with regard to the Energy Efficiency Act (every 3 years or 12 years).
Definitions
Qualified person:
A person who can demonstrate certain certificates of competence in a specialist area (examination provided for this purpose).
Only qualified persons may carry out maintenance work on refrigeration systems.
Competent person:
Instructed person who can rely on their practical experience, on one thing and on one person.




